2.8 RCS protocols / RCS协议
The following table summarises the list of protocols employed by RCS clients. It must be noted that the choice among the options presented will not impact Service Provider interoperability:
下表总结了RCS客户端使用的协议列表。 必须注意的是,所提供的选项之间的选择不会影响服务提供商的互操作性:
| Protocol name | Description | Transport layer | Secure transport layer/protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Session initiation protocol (SIP) | Client-IMS core signalling protocol | User Datagram Protocol (UDP) over IP or Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) over IP | SIP over Transport Layer Security (TLS) or IP Security (IPsec) |
| Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP) | Chat messages, media (pictures) and file exchange protocol | TCP/IP | MSRP over TLS |
| Real-time protocol (RTP) | Real Time Media (voice and video) exchange | UDP/IP | Secure RTP (SRTP) (see [RFC3711]) |
| Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) | Access to Message Store Server | TCP/IP | IMAP over TLS |
| Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) | XML configuration access protocol (XCAP) transactions HTTP configuration mechanism | TCP/IP | HTTPS |
Table 25: RCS protocols / 表25:RCS协议
According to [RFC3261] RCS clients shall support both SIP/UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and SIP/TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). The choice of whether both are used or only TCP is used to transport the signalling data belongs to each Service Provider and is controlled by the configuration parameters “psSignalling”, “psSignallingRoaming” and “wifiSignalling” in [PRD-RCC.15] section 2.2.2.2.
根据[RFC3261],RCS客户端应同时支持SIP/UDP(用户数据报协议)和SIP/TCP(传输控制协议)。 客户端可以选择同时使用TCP/UDP,或仅使用TCP,来传输属于每个服务提供商的信令数据,该选择由[PRD-RCC.15]中的2.2.2.2节中的配置参数“psSignalling”,“psSignallingRoaming”和“wifiSignalling” 来控制。
NOTE: The “psSignallingRoaming” parameter is defined as a temporary workaround to address PS roaming related issues identified in live deployments.
注意:“psSignallingRoaming”参数定义为临时解决方法,以解决实时部署中识别的PS漫游相关问题。
Regarding the impact of Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal in the different protocols involved in RCS, the following considerations shall be taken into account:
关于在RCS中涉及的不同协议中的网络地址转换(NAT)遍历的影响,应考虑以下意见:
- Regarding the SIP protocol:
关于SIP协议:- Carriage Return Line Feed (CRLF) keep-alive [RFC6223] support is MANDATORY when only SIP/TCP or SIP/TLS is used by the RCS client and SIP/UDP is not used. Section C.1 describes how both client and server could initiate the sending of the keep alives.
当RCS客户端仅使用SIP/TCP或SIP/TLS并且未使用SIP/UDP时,回车换行(CRLF)keep-alive[RFC6223]支持是强制的。 C.1节描述了客户端和服务器如何可以发起保持活动的发送。 - Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (STUN) keep-alive [RFC6223] support is RECOMMENDED when SIP/UDP is used by the RCS client as it allows network capacity optimization.
当SIP/UDP由RCS客户端使用时,推荐使用UDP通过NAT的简单穿越(STUN)保持活动[RFC6223]支持,因为它允许网络容量优化。 - An RCS client using SIP/UDP:
使用SIP / UDP的RCS客户端:- Shall support symmetric signalling (That is the IP and port combination used to send SIP messages is the same as the one used to receive SIP messages).
应支持对称信令(即用于发送SIP消息的IP和端口组合与用于接收SIP消息的IP和端口组合相同)。 - Shall perform TCP switchover for large SIP messages.
应对大型SIP消息执行TCP切换。
- Shall support symmetric signalling (That is the IP and port combination used to send SIP messages is the same as the one used to receive SIP messages).
- Carriage Return Line Feed (CRLF) keep-alive [RFC6223] support is MANDATORY when only SIP/TCP or SIP/TLS is used by the RCS client and SIP/UDP is not used. Section C.1 describes how both client and server could initiate the sending of the keep alives.
- For handling Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP) sessions, the RCS MSRP endpoints shall support:
为了处理消息会话中继协议(MSRP)会话,RCS MSRP端点应支持:- [RFC6135]: “The Alternative Connection Model for the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)”
[RFC6135]:“消息会话中继协议(MSRP)的备用连接模型” - The mechanisms described in section 2.8.2 regarding session matching for MSRP.
在第2.8.2节中描述的关于MSRP的会话匹配的机制。 - For NAT traversal for MSRP, keep alives (i.e. empty MSRP packets) are not necessary. If the TCP connection is torn down because of inactivity, the MSRP session is torn down, and a new SIP INVITE request to set up a new MSRP session is sent the next time a message is to be sent.
对于MSRP的NAT穿越,保持活动(即空MSRP包)不是必需的。 如果TCP连接由于不活动而被断开,则MSRP会话被拆除,并且在下一次要发送消息时发送用于建立新的MSRP会话的新的SIP INVITE请求。
- [RFC6135]: “The Alternative Connection Model for the Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP)”
- Regarding NAT traversal of Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) sessions, the RCS client should implement the mechanism described in section 2.8.1.
关于实时传输协议(RTP)会话的NAT穿越,RCS客户端应该实现第2.8.1节中描述的机制。 - For Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) and HTTP no specific mechanisms are mandated in the current specification to support NAT traversal.
对于Internet邮件访问协议(IMAP)和HTTP,在当前规范中不强制要求特定机制来支持NAT遍历。
The support of Transport Layer Security (TLS) based or IP Security (IPsec) based protocols to secure the signalling and TLS based for MSRP and IMAP protocols or Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) for RTP protocols to secure media exchanges is recommended particularly for those scenarios where the data is carried over a network outside the Service Provider domain (i.e. Wi-Fi access). For more information on access security, see section 2.13.
建议特别支持基于传输层安全(TLS)或基于IP安全(IPsec)的协议以确保用于MSRP和IMAP协议的信令和TLS,或用于RTP协议的安全实时传输协议(SRTP)用于安全的媒体交换 对于其中数据通过服务提供商域外的网络(即Wi-Fi接入)承载的那些情况。 有关访问安全性的更多信息,请参阅第2.13节。
NOTE: To ensure interoperability of all RCS capable devices across different Service Provider networks, the list of preferred options for the transport and security for the signalling and media protocols is included in the configuration parameters as defined in [PRD-RCC.15], section 2.2.2.2.
注意:为确保跨不同服务提供商网络的所有支持RCS的设备的互操作性,用于信令和媒体协议的传输和安全性的首选选项列表包含在配置参数中,如[PRD-RCC.15]章节 2.2.2.2。
Consequently, a Service Provider provides this information as part of the first-time or re-configuration scenarios described in section 2.3.
因此,服务提供商提供此信息作为第2.3节中描述的第一次或重新配置方案的一部分。
2.8.1 RTP and NAT traversal / RTP和NAT穿越
As mentioned previously, an RCS client must implement several mechanisms to avoid the negative impact of NAT traversal, which can both occur when connecting over:
如前所述,RCS客户端必须实现几种机制,以避免NAT穿越的负面影响,负面影响会在通过以下两种连接方式时发生:
- PS: Mainly due to the scarcity of IPv4 public addresses and proxying performed at APN level, or,
PS:主要是由于IPv4公共地址稀缺和在APN级别执行代理,或者, - Wi-Fi: In this case due to the fact the network topology between the access point and the Internet may vary between deployments.
Wi-Fi:在这种情况下,由于接入点和Internet之间的网络拓扑在部署之间可能不同。
To combat the negative effects of NAT traversal on the RTP protocol, the RCS client:
为了克服NAT穿越对RTP协议的负面影响,RCS客户端:
- Shall support a keep-alive mechanism to open and maintain the NAT binding alive regardless of whether the media stream is currently inactive, send-only, receive-only or send-receive. The recommended standard keep-alive mechanism is an empty (no payload) RTP packet with a payload type of 20 (as per [3GPP TS 24.229]).
将支持保持活动机制以打开和保持NAT绑定活着,而不管媒体流当前是不活动的,仅发送,仅接收还是发送接收。 推荐的标准保持活动机制是有效载荷类型为20的空(无有效载荷)RTP分组(根据[3GPP TS 24.229])。- SHALL when sending empty packets instead of using STUN and it is about to receive a Video Stream send these dummy RTP packets at a high rate (recommended rate: 50 to 100ms) from the moment the SIP INVITE request is received (or the 180 RINGING is sent) in bursts sent regularly (a 1 second burst every 15 seconds is recommended). This shall be done until one of the following conditions is met:
当发送空分组而不是使用STUN并且它即将接收视频流时,从接收到SIP INVITE请求的时刻开始以高速率(推荐速率:50到100ms)发送这些虚拟RTP分组(或者180RINGING是 发送)定期发送(建议每15秒发送1秒)。 这应该完成,直到满足以下条件之一:- The first RTP packet of a Video Stream is received, or,
接收视频流的第一RTP分组,或者, - The client starts streaming itself in case of a bi-directional RTP stream, or,
在双向RTP流的情况下,客户端开始流传输本身,或者, - A final response is sent on the SIP INVITE request. In case this final response is a 200 OK response, the client shall continuously send the dummy RTP packets until either the first RTP packet of a Video Stream is received or the client starts streaming itself in case of a bi-directional RTP stream.
在SIP INVITE请求上发送最终响应。 在该最终响应是200OK响应的情况下,客户端将连续发送虚拟RTP分组,直到接收到视频流的第一RTP分组或者在双向RTP流的情况下客户端开始流传输本身。
Once the first RTP packet is received the dummy packets shall be sent at a lower rate (a transmission every 15 sec is recommended) for the remainder of a uni-directional session or not at all in case the RTP stream is bi-directional.
一旦接收到第一RTP分组,对于单向会话的剩余部分,或者在RTP流是双向的情况下,虚拟分组应当以更低的速率(对于单向会话的剩余部分,每隔15秒的传输)发送。
- The first RTP packet of a Video Stream is received, or,
- If the first frame is not an I-Frame or Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) unit carrying a Sequence Parameter Set (SPS) or Picture Parameter Set (PPS), the receiving client SHALL send a RTCP Full Intra Request (FIR) (see [RFC5104], section 4.3.1) to the sender.
如果第一帧不是携带序列参数集(SPS)或图像参数集(PPS)的I帧或网络抽象层(NAL)单元,则接收客户端应发送RTCP全内部请求(FIR)(参见[RFC5104],第4.3.1节)。 - SHALL reset the encoder as specified in [RFC5104] when receiving an RTCP FIR, and send SPS, PPS (if not provided in the SDP) and an I-Frame to the receiver.
当接收到RTCP FIR时,应重置[RFC5104]中规定的编码器,并向接收器发送SPS,PPS(如果在SDP中未提供)和I帧。
- SHALL when sending empty packets instead of using STUN and it is about to receive a Video Stream send these dummy RTP packets at a high rate (recommended rate: 50 to 100ms) from the moment the SIP INVITE request is received (or the 180 RINGING is sent) in bursts sent regularly (a 1 second burst every 15 seconds is recommended). This shall be done until one of the following conditions is met:
Shall use symmetric media (that is use the same port number for sending and receiving packets) as defined in [RFC4961] mechanism which is summarized below:
应使用[RFC4961]机制中定义的对称媒体(即使用相同的端口号发送和接收数据包),总结如下:- When an invitation for Video Share is received and accepted, the 200 OK response contains a SDP body containing all the necessary fields (including the destination port) for the sender to send the RTP packets.
当接收并接受视频共享邀请时,200 OK响应包含SDP主体,其包含发送方发送RTP分组所需的所有字段(包括目的地端口)。 - Immediately after sending the 180 Ringing response, the receiver will send a keep-alive packet back to the sender to secure the timely setup of the media path:
在发送180振铃响应之后,接收器立即向发送器发送保活分组以保证媒体路径的及时建立: - The source port shall be identical to the one included in the m field of the SDP payload inside the 200 OK response.
源端口应与200 OK响应内部的SDP有效载荷的m字段中包含的源端口相同。 - The destination port shall be identical to the one included in the m field of the SDP payload inside the SIP INVITE message.
目的地端口应与SIP INVITE消息内部的SDP有效载荷的m字段中包括的一个相同。- The sender should allow enough time for the media path to be secured.
发送方应该有足够的时间保证媒体路径。
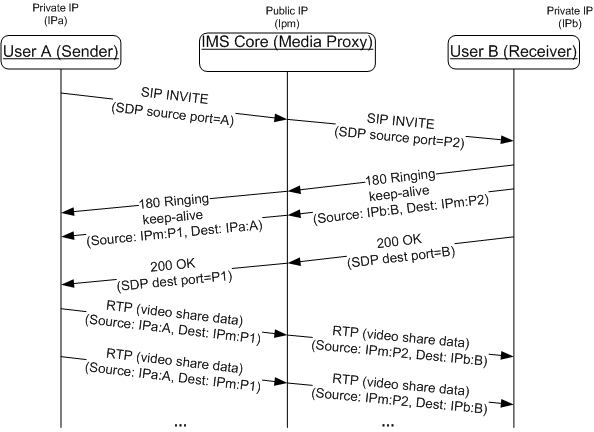
Figure 17: RTP symmetric media path establishment / 图17:RTP对称媒体路径建立NOTE1: as a general recommendation, User A should also send a keep-alive once it receives the SDP from the other side.
注1:作为一般建议,用户A一旦从另一侧接收到SDP,还应发送保持活动。
- The sender should allow enough time for the media path to be secured.
- When an invitation for Video Share is received and accepted, the 200 OK response contains a SDP body containing all the necessary fields (including the destination port) for the sender to send the RTP packets.
Shall use the Real-Time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP):
应使用实时传输控制协议(RTCP):
The symmetric media procedure described for the RTP protocol is, in general, applicable to any UDP stream. As the usage of RTCP is also mandatory, an analogous mechanism shall be implemented to prevent any RTCP streams from being blocked. Therefore, the symmetric media procedure described in this section for RTP is also applicable to RTCP and shall be employed (that is a dummy packet is sent by the receiver to secure the RTP flow and a second one is used to secure the RTCP flow). Also the sender device/client shall send a dummy packet when the session is established to secure the RTCP flow on their side and ensure the reception of any RTCP RR (Receiver Report) sent by the receiving side. The dummy packet format recommended for establishing the RTCP flow is an empty RTCP RR or empty RTCP SR (Sender Report).
针对RTP协议描述的对称媒体过程通常适用于任何UDP流。 由于RTCP的使用也是强制性的,因此应当实现类似的机制以防止任何RTCP流被阻塞。 因此,本部分中描述的用于RTP的对称媒体过程也适用于RTCP并且将被采用(即,由接收器发送虚拟分组以保护RTP流,并且第二个用于保护RTCP流)。 此外,当建立会话时,发送方设备/客户端应发送虚拟分组,以保证其侧的RTCP流安全,并确保接收方发送的任何RTCP RR(接收方报告)。 推荐用于建立RTCP流的伪分组格式是空RTCP RR或空RTCP SR(发送方报告)。NOTE2: For a VoLTE/VoWiFi enabled device, RTCP usage for a voice session shall be as defined in section 3.2.4 of [PRD-IR.92]
注2:对于支持VoLTE/VoWiFi的设备,语音会话的RTCP使用应如[PRD-IR.92]第3.2.4节所定义。
Please note that for readability purposes, the procedures described in this section have not been included in the diagrams in section 3.6 covering the Video Share functionality.
请注意,出于可读性的目的,本节中描述的过程未包含在包含视频共享功能的第3.6节中的图中。
2.8.2 MSRP session matching / MSRP会话匹配
NOTE: The text in this section is based on the text contained in the now expired IETF internet draft draft-ietf-simple-msrp-sessmatch-10.
注意:本节中的文本基于现在已过期的IETF互联网草案draft-ietf-simple-msrp-sessmatch-10中包含的文本。
When the CHAT MESSAGING TECHNOLOGY configuration parameter defined in Table 75 is set to use OMA CPM, an RCS client shall set up MSRP sessions as per [RCS-CPM-CONVFUNC-ENDORS]. Otherwise, the session shall be set up according to the procedures in [RFC4975], [RFC6135] and the procedure in this section for the session matching.
当表75中定义的CHAT MESSAGING TECHNOLOGY配置参数被设置为使用OMA CPM时,RCS客户端将按照[RCS-CPM-CONVFUNC-ENDORS]建立MSRP会话。 否则,应根据[RFC4975],[RFC6135]中的过程和本节中的过程来建立会话以进行会话匹配。
This section defines how an MSRP entity (e.g. an RCS Client, Messaging Server or other node handling MSRP within the network) that does not support the procedures in [RCS-CPM-CONVFUNC-ENDORS] or is configured not to use them matches an incoming MSRP message to an MSRP session. The difference between the session matching mechanism in [RFC4975] and the one defined here is that while the mechanism in [RFC4975] uses the MSRP URI comparison rules for session matching, for RCS, only the session-id part of the MSRP URI is used.
本节定义不支持[RCS-CPM-CONVFUNC-ENDORS]中的过程或被配置为不使用它们的MSRP实体(例如,RCS客户端,消息服务器或处理网络内的MSRP的其他节点)如何匹配入局 MSRP消息发送到MSRP会话。 [RFC4975]中的会话匹配机制和这里定义的会话匹配机制之间的区别是,虽然[RFC4975]中的机制使用MSRP URI比较规则进行会话匹配,但对于RCS,仅使用MSRP URI的会话ID部分 。
When an MSRP entity receives the first MSRP request for an MSRP session, the To-Path header field of the request should contain a URI with a session-id part that was provided in the SDP associated with the MSRP session. The entity that accepted the connection looks up the session-id part of the MSRP URI in the received requests, in order to determine which session it matches. The session-id part is compared as case sensitive. If a match exists, the entity shall assume that the host that formed the connection is the host to which this URI was given. If no match exists, the entity shall reject the request with a 481 error response. The entity shall also check to make sure the session is not already in use on another connection. If the session is already in use, it shall reject the request with a 506 error response.
当MSRP实体接收到针对MSRP会话的第一MSRP请求时,该请求的To-Path头字段应该包含具有在与MSRP会话相关联的SDP中提供的会话id部分的URI。 接受连接的实体在接收的请求中查找MSRP URI的会话ID部分,以确定它匹配哪个会话。 会话ID部分作为区分大小写进行比较。 如果存在匹配,则实体应假设形成连接的主机是给定该URI的主机。 如果不存在匹配,则实体将以481错误响应拒绝请求。 实体还应检查以确保会话尚未在另一个连接上使用。 如果会话已经在使用,它将拒绝该请求与506错误响应。
2.8.3 SIP Issues / SIP问题
- An RCS client should use a random originating SIP signalling port of the range 1025- 65535. If the selected port is not available, the next port number shall be used for this session.
RCS客户端应使用范围为1025-65535的随机始发SIP信令端口。如果所选端口不可用,则下一个端口号应用于此会话。 - An RCS client shall build its SIP contact address to be unique. A recommended way to do so is to use a hashed value of the +sip.instance tag as user part of the URI of the contact address.
RCS客户端应建立其SIP联系地址是唯一的。 推荐的方法是使用+sip.instance标记的散列值作为联系人地址的URI的用户部分。 - For an incoming request, an RCS client should verify that the Request-URI matches the URI of its registered contact address. If not, the Request-URI shall be considered an unexpected address and the request shall be rejected as per [RFC3261] section 8.2.2.1.
对于传入请求,RCS客户端应验证Request-URI是否与其注册的联系地址的URI匹配。 如果不是,Request-URI将被认为是一个意外的地址,根据[RFC3261]第8.2.2.1节,该请求将被拒绝。