2.13 Security and privacy / 安全和隐私
2.13.1 Access Security for the User-to-Network Interface (UNI) / 用户到网络接口(UNIT)的访问安全性
2.13.1.1 Access Signalling Security Methods / 访问信令安全方法
Several SIP signalling access security and authentication methods are specified in [3GPP TS 33.203] and [3GPP TS 24.229] for access to the IMS core and IMS based services such as RCS. The applicability and choice of method is highly dependent on the RCS client and access type (e.g. trusted or untrusted) including what is supported or required by the IMS core.
在[3GPP TS 33.203]和[3GPP TS 24.229]中规定了用于接入IMS核心和基于IMS的服务(例如RCS)的几种SIP信令接入安全和认证方法。 方法的适用性和选择高度依赖于RCS客户端和接入类型(例如,可信或不可信),包括IMS核心所支持或要求的内容。
2.13.1.1.1 IMS AKA with IPsec / 具有IPsec的IMS AKA
IMS AKA with IPsec is the preferred long term approach in IMS for access signalling security from a cellular PS network. Such access requires the IMS client device to possess an AKA based credential (e.g. Universal SIM (USIM)/IP Multimedia Services SIM (ISIM)) and support the “ipsec-3gpp” procedures specified in [3GPP TS 33.203] and [3GPP TS 24.229].
具有IPsec的IMS AKA是IMS中用于来自蜂窝PS网络的接入信令安全性的优选长期方法。 这种接入要求IMS客户端设备拥有基于AKA的凭证(例如通用SIM(USIM)/ IP多媒体服务SIM(ISIM))并且支持[3GPP TS 33.203]和[3GPP TS 24.229]中规定的“ipsec-3gpp”过程。
IMS AKA with IPsec is the access signalling approach specified for Voice over LTE (VoLTE) ([PRD-IR.92]).
具有IPsec的IMS AKA是为LTE上的语音(VoLTE)([PRD-IR.92])规定的接入信令方法。
2.13.1.1.2 SIP Digest Authentication and TLS / SIP摘要认证和TLS
SIP Digest is a username and password challenge based authentication (based on HTTP Digest) which is suited for broadband access to IMS or for RCS clients which do not possess AKA based credentials (e.g. xSIM) or do not support IMS AKA based IPsec. SIP Digest is widely implemented in Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) based SIP clients and is often deployed with TLS. Support for SIP Digest with and without TLS is specified in [3GPP TS 33.203] and [3GPP TS 24.229] for access to IMS from “non-3gpp” defined access networks (e.g. broadband/fixed access networks).
SIP摘要是基于用户名和密码挑战的认证(基于HTTP摘要),其适合于宽带接入IMS或不具有基于AKA的凭证(例如xSIM)或不支持基于IMS AKA的IPsec的RCS客户端。 SIP摘要在基于互联网工程任务组(IETF)的SIP客户端中广泛实现,并且经常部署有TLS。 在[3GPP TS 33.203]和[3GPP TS 24.229]中规定了对具有和不具有TLS的SIP摘要的支持,用于从“非3gpp”定义的接入网络(例如宽带/固定接入网络)接入IMS。
When an RCS client is enabled for SIP Digest authentication, the client will use the pre- configured SIP username and password as specified in Table 79 to authenticate to the IMS core. For the initial SIP REGISTER message (before a digest challenge), the RCS client shall include an authorisation header (as per [3GPP TS 24.229]) which includes the SIP digest username and an empty digest authentication response parameter. This allows the IMS core to treat the SIP digest username as an IMS private user identity (IMPI) which is distinct from the IMS public user identity (IMPU), allowing the same SIP public user identity (or IMPU) to be registered from multiple RCS clients/devices.
当RCS客户端启用SIP摘要身份验证时,客户端将使用表79中指定的预配置SIP用户名和密码对IMS核心进行身份验证。 对于初始SIP REGISTER消息(在摘要质询之前),RCS客户端将包括授权报头(根据[3GPP TS 24.229]),其包括SIP摘要用户名和空摘要认证响应参数。 这允许IMS核心将SIP摘要用户名作为不同于IMS公共用户身份(IMPU)的IMS私有用户身份(IMPI),允许从多个RCS注册相同的SIP公共用户身份(或IMPU) 客户端/设备。
The IMS registration flow for SIP digest authentication is shown in Figure 20. In this example flow, the RCS client is connected to the IMS core over a Wi-Fi internet broadband connection.
用于SIP摘要认证的IMS注册流程如图20所示。在该示例流程中,RCS客户端通过Wi-Fi因特网宽带连接连接到IMS核心。
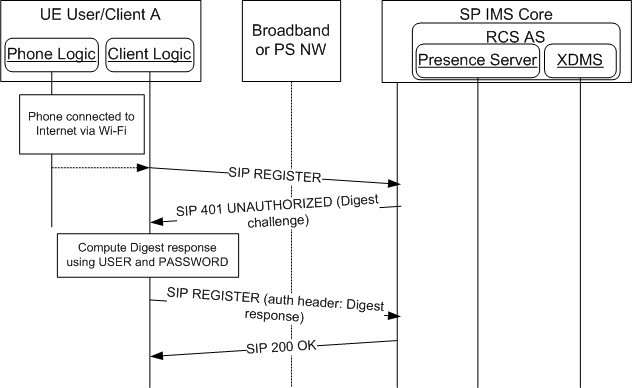
Figure 20: Registration with SIP Digest Authentication / 图20:使用SIP摘要身份验证注册
If digest authentication fails two times with a SIP 401 UNAUTHORISED response, the client shall not attempt further registration attempts, but rather consider the current configuration as invalid and force a reconfiguration using the procedures in chapter 2.3 the next time the handset is rebooted.
如果摘要身份验证在SIP 401 UNAUTHORIZED响应中失败两次,则客户端不应尝试进一步的注册尝试,而是将当前配置视为无效,并在下次手持设备重新启动时使用第2.3章中的过程强制重新配置。
The use of SIP Digest with TLS is recommended for access from untrusted access networks (including WLAN with no encryption). TLS provides per message authentication, integrity protection and encryption for SIP signalling. TLS with server side certificates also provides authentication of the IMS core to the RCS client.
建议使用SIP Digest with TLS来从不受信任的接入网络(包括没有加密的WLAN)进行接入。 TLS为SIP信令提供每个消息认证,完整性保护和加密。 具有服务器端证书的TLS还向RCS客户端提供IMS核心的认证。
NOTE: This requires the client to possess a root or intermediate certificate of a Certificate Authority (CA) that is in the certificate signing chain for the IMS core’s (e.g. P-CSCF) TLS certificate.
注意:这要求客户端拥有IMS核心(例如P-CSCF)TLS证书的证书签名链中的证书颁发机构(CA)的根证书或中间证书。
When an RCS client is enabled to use SIP/TLS it should use the SIP TLS port obtained through P-CSCF discovery procedures (e.g. through DNS SRV records [Service records]) or configuration. However, if RCS client is not able to determine a SIP TLS port through these means, it shall use the default SIP port for TLS as specified in [RFC3261].
当RCS客户端被使能使用SIP / TLS时,它应该使用通过P-CSCF发现过程(例如通过DNS SRV记录[Service records])或配置获得的SIP TLS端口。但是,如果RCS客户端不能通过这些手段确定SIP TLS端口,则应使用[RFC3261]中指定的TLS的默认SIP端口。
The RCS client enabled to use SIP/TLS should first use the SIP security agreement (sec- agree) [RFC3329] as specified in [3GPP TS 24.229] to first negotiate the use of TLS with its SIP Proxy (P-CSCF). Alternatively, an RCS client may first try to establish a TLS session with the SIP proxy (P-CSCF) before sending an initial SIP Register message which does not include sec-agree for TLS. However, with this approach the S-CSCF may challenge subsequent non-Register messages with a 407 Proxy Authentication Required unless configured to trust SIP Digest without signalling security indicated or if the P-CSCF is able to provide this indication despite not using sec-agree.
启用使用SIP / TLS的RCS客户端应首先使用[3GPP TS 24.229]中指定的SIP安全协议(sec-agree)[RFC3329]首先协商与其SIP代理(P-CSCF)使用TLS。 或者,RCS客户端可以首先尝试在发送不包括TLS同意的初始SIP注册消息之前与SIP代理(P-CSCF)建立TLS会话。 然而,利用该方法,S-CSCF可以用407代理认证要求来挑战随后的非注册消息,除非被配置为在没有指示的信令安全的情况下信任SIP摘要,或者即使P-CSCF能够提供该指示,尽管不使用sec-agree 。
NOTE: In both cases SIP proxy (P-CSCF) authenticates to the RCS client using a TLS server certificate.
注意:在这两种情况下,SIP代理(P-CSCF)使用TLS服务器证书向RCS客户端进行身份验证。
When SIP Digest is not used with TLS, the IMS core may require non-REGISTER SIP requests to be authenticated using the same SIP Digest challenge mechanisms used during registration. However, in this case the SIP digest challenge is sent in a 407 (Proxy Authentication Required) response. An RCS client that receives a 407 (Proxy Authentication Required) response shall respond by sending an authenticated SIP request which includes a Proxy Authorization header with the digest response. The RCS client shall cache the digest challenge data (e.g. server nonce) for use in authenticating subsequent SIP requests using a nonce-count value (for replay protection) as per [RFC2617] and including a Proxy Authorization header with an updated digest response. This avoids the need for the IMS core to challenge each SIP request before the authentication data expires. Once the digest authentication data expires a new challenge will be issued.
当SIP摘要不与TLS一起使用时,IMS核心可以要求使用在注册期间使用的相同的SIP摘要询问机制来认证非REGISTER SIP请求。 然而,在这种情况下,在407(需要代理认证)响应中发送SIP摘要质询。 接收407(需要代理认证)响应的RCS客户端将通过发送包括具有摘要响应的代理授权报头的经认证的SIP请求来响应。 RCS客户端将使用根据[RFC2617]的随机数计数值(用于重放保护)并且包括具有更新的摘要响应的代理授权报头,缓存摘要询问数据(例如,服务器随机数)以用于认证后续SIP请求。 这避免了IMS核心在认证数据到期之前挑战每个SIP请求的需要。 一旦摘要认证数据到期,将发出新的挑战字符串。
NOTE: The IMS core may also support binding the RCS client’s IMS identities authenticated during registration with a source IP address (and port if [RFC5626] “SIP Outbound” is used). In such cases, the IMS core may not require subsequent non-registration based SIP messaging to be authenticated using SIP Digest if the identities and source addresses in the messaging matches the binding obtained during the Digest authenticated registration process.
注意:IMS核心还可以支持在注册期间验证的RCS客户端的IMS身份与源IP地址(以及使用[RFC5626]“SIP Outbound”时的端口)绑定。 在这种情况下,如果消息中的身份和源地址与在Digest认证注册过程期间获得的绑定匹配,则IMS核心可以不要求使用SIP摘要来对随后的基于非注册的SIP消息传递进行认证。
2.13.1.2 Access Signalling Security Profiles for RCS / RCS的访问信令安全配置文件
As there are several considerations which access signalling security method should be used for access to RCS services, the following table defines authentication and access signalling security mechanisms as per RCS device and access type.
由于应该使用接入信令安全方法来接入RCS服务有几个考虑因素,下表根据RCS设备和接入类型定义了认证和接入信令安全机制。
| Device | Access | Applicable Security Methods | Applicability and Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile client not configured for VoLTE/VoWiFi | Cellular PS Access | SIP Digest (with or without TLS) or IMS AKA with IPsec | IMS AKA with IPSec may be used when supported by both device and the network. SIP Digest with or without TLS is used depending on (pre-)configuration |
| access over EPC-integrated Wi-Fi | SIP Digest (with or without TLS) or IMS AKA with IPsec | IMS AKA with IPSec may be used when supported by both device and the network. SIP Digest with or without TLS is used in cases when pre-configured | |
| Non-cellular broadband (Wi-Fi) access | SIP Digest, SIP Digest with TLS or IMS AKA with IPsec | SIP Digest with TLS is recommended over SIP Digest without TLS SIP Digest with or without TLS is used in cases when pre-configured or when the mobile device does not support IMS AKA for WLAN access | |
| VoLTE/VoWiFi configured mobile client | Cellular PS Access | SIP Digest, SIP Digest with TLS or IMS AKA with IPsec27 as specified in [PRD-NG.102] NOTE: The configuration to any other method is not possible. | AKA credentials stored securely in a UICC such as an xSIM. The method used depends on the relation to the registration for VoLTE/VoWiFi (see [PRD-NG.102]) |
| EPC-integrated Wi-Fi | SIP Digest, SIP Digest with TLS or IMS AKA with IPsec[27] as specified in [PRD-NG.102] NOTE: The configuration to any other method is not possible. | AKA credentials stored securely in a UICC such as an xSIM. The method used depends on the relation to the registration for VoLTE/VoWiFi (see [PRD-NG.102]) | |
| Non-cellular broadband (Wi-Fi) access | SIP Digest, SIP Digest with TLS or IMS AKA with IPsec[27]. | SIP Digest with TLS is recommended over SIP Digest without TLS SIP Digest with or without TLS is used in cases when pre-configured or when the mobile device does not support IMS AKA for WLAN access. | |
| Broadband Access Enabled | SIP Digest or SIP Digest with TLS | SIP Digest with TLS is recommended over SIP Digest without TLS SIP Digest is used for mobile devices which do not support IMS AKA for WLAN access. |
[27] Requires UDP encapsulation of IPsec for NAT traversal
[27] 需要UDP封装IPsec才能进行NAT穿越
For RCS devices which can access the IMS core from both mobile and broadband/fixed networks (e.g. Wi-Fi) a separate access signalling security method and corresponding authentication credential may be required. If the security mechanism is not pre-configured as per section 2.2.1.1.2 and 2.2.2.1.3 of [PRD-RCC.15], the RCS device negotiates the set of security mechanisms using the SIP security agreement [RFC3329] as specified for IMS in [3GPP TS 33.203] and [3GPP TS 24.229]. If the client is pre-configured with a specific access signalling security mechanism, the client uses the signalling corresponding to this security method in the initial registration procedure, and the IMS core determines (based on signalling) which mechanism is being used/requested and then determines (based on security policy) if the access signalling security method is allowed.
对于可以从移动和宽带/固定网络(例如Wi-Fi)接入IMS核心的RCS设备,可能需要单独的接入信令安全方法和相应的认证证书。 如果安全机制没有根据[PRD-RCC.15]的2.2.1.1.2和2.2.2.1.3预先配置,则RCS设备使用SIP安全协议[RFC3329]协商一组安全机制 在[3GPP TS 33.203]和[3GPP TS 24.229]中为IMS指定。 如果客户端被预配置有特定的接入信令安全机制,则客户端在初始注册过程中使用与该安全方法相对应的信令,并且IMS核心(基于信令)确定正在使用/请求哪个机制,然后 (基于安全策略)确定是否允许接入信令安全方法。
NOTE: The RCS device shall support a configuration option for each of these profiles (where applicable).
注意:RCS设备应支持每个配置文件的配置选项(如果适用)。
2.13.1.3 Access Media Security / 访问媒体安全
2.13.1.3.1 Secure RTP (SRTP) / 安全RTP(SRTP)
SRTP [RFC3711] may be used to provide per message authentication, integrity protection and encryption for both RTP and RTCP streams involved in real-time video and voice sessions. The use of SRTP is recommended for communications over any untrusted network in which confidentiality (or lack of) is a concern. As an example, a voice or video call over a Wi-Fi network (e.g. “Hot Spot”) without any WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) encryption is highly susceptible to eavesdropping.
SRTP [RFC3711]可用于为实时视频和语音会话中涉及的RTP和RTCP流提供每个消息认证,完整性保护和加密。 建议使用SRTP用于任何不受信任的网络中的通信,其中涉及机密性(或缺乏)。 作为示例,在没有任何WLAN(无线局域网)加密的情况下通过Wi-Fi网络(例如“热点”)的语音或视频呼叫非常容易被窃听。
The establishment and key exchange for SRTP in RCS shall be based on SDES (Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions for Media Streams, cf. [RFC4568]) which is transported within SDP, following the SIP SDP offer/answer model. SDES and SRTP profiles for media security in IMS are specified in [3GPP TS 33.328].
在RCS中的SRTP的建立和密钥交换将基于在SDP提供/应答模型之后在SDP内传输的SDES(用于媒体流的会话描述协议安全描述,参见[RFC4568])。 在[3GPP TS 33.328]中规定了用于IMS中的媒体安全性的SDES和SRTP简档。
NOTE: [3GPP TS 33.328] defines two modes of operation for SDES/SRTP: e2ae (end-to-access edge) mode and e2e (end-to-end) mode. For the e2ae mode, SDES is run between an IMS client and a SIP edge proxy, i.e. a P- CSCF (IMS-ALG). An IMS access Gateway controlled by a P-CSCF (IMS- ALG [Application Layer Gateway]) provides the SRTP termination for the “Access Edge”. In the e2e mode, SDES and SRTP is transported end-end between two end user clients.
注意:[3GPP TS 33.328]定义了SDES / SRTP的两种操作模式:e2ae(端到端边缘)模式和e2e(端到端)模式。 对于e2ae模式,SDES在IMS客户端和SIP边缘代理之间运行,即P-CSCF(IMS-ALG)。 由P-CSCF(IMS-ALG [应用层网关])控制的IMS接入网关为“接入边缘”提供SRTP终止。 在e2e模式下,SDES和SRTP在两个终端用户客户端之间端到端传输。
An RCS client that supports SRTP and SDES and support e2ae mode shall indicate this during the IMS registration according to [3GPP TS 24.229]. The P-CSCF (IMS ALG), if supporting e2ae mode, indicates this to the UE as part of the IMS registration procedures according to [3GPP TS 24.229]. The use of SRTP is enabled through the client configuration parameters (see section A.2.10), and whether it is used or not can be configured differently for Wi-Fi access and cellular access.
支持SRTP和SDES并且支持e2ae模式的RCS客户端将在根据[3GPP TS 24.229]的IMS注册期间指示这一点。 如果支持e2ae模式,则P-CSCF(IMS ALG)将此指示给UE,作为根据[3GPP TS 24.229]的IMS注册过程的一部分。 通过客户端配置参数(请参阅第A.2.10节)启用SRTP的使用,以及是否使用SRTP可以针对Wi-Fi接入和蜂窝接入进行不同配置。
However not all end user clients may support SRTP. Therefore, the Service Provider’s network equipment should support e2ae mode. An RCS client that supports SRTP and SDES shall also support e2ae mode.
但并非所有最终用户客户端都可以支持SRTP。 因此,服务提供商的网络设备应支持e2ae模式。 支持SRTP和SDES的RCS客户端还应支持e2ae模式。
When using SRTP/SDES, the RCS client can include preference of security mode to use in accordance to [3GPP TS 33.328]. It is recommended that e2ae mode is used by the UE, if also indicated to be supported by the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG). Otherwise, the RCS client may try e2e by not indicating any preference during the session setup.
当使用SRTP / SDES时,RCS客户端可以包括根据[3GPP TS 33.328]使用的安全模式的优先级。 如果还指示由P-CSCF(IMS-ALG)支持,则推荐e2ae模式由UE使用。 否则,RCS客户端可以在会话建立期间不指示任何偏好来尝试e2e。
NOTE: This does not exclude that the Service Provider network still may decide to terminate the media security in the network (P-CSCF (IMS-ALG)).
注意:这并不排除服务提供商网络仍然可能决定终止网络中的媒体安全性(P-CSCF(IMS-ALG))。
For terminating sessions, when the UE has indicated support for e2ae SRTP/SDES in the registration, the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) shall behave as specified in [3GPP TS 24.229], i.e. ensure that SRTP is used, and facilitate interworking from RTP to SRTP when needed.
对于终止会话,当UE在注册中指示对e2ae SRTP / SDES的支持时,P-CSCF(IMS-ALG)应当如[3GPP TS 24.229]中所规定的那样行使,即确保使用SRTP,并且促进从 RTP到SRTP(需要时)。
For terminating session, when the UE has not indicated support for e2ae SRTP/SDES, the P-CSCF (IMS ALG) decides based on local policy, whether to apply SRTP / SDES towards the UE. A possible local policy is that the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) invokes procedures related to SDP and SRTP for Wi-Fi access, but not for cellular access.
对于终止会话,当UE没有指示支持e2ae SRTP / SDES时,P-CSCF(IMS ALG)基于本地策略来决定是否向UE应用SRTP / SDES。 可能的本地策略是P-CSCF(IMS-ALG)调用与用于Wi-Fi接入的SDP和SRTP相关的过程,但不用于蜂窝接入。
NOTE: Enforcing SRTP/SDES on the terminating call leg towards a UE that does not support SRTP/SDES will lead to the connection establishment failing, which may be an issue for inbound roaming where the operator has no control of what clients are used, or for cases where there are other (non- RCS) clients in the same network that use RTP.
注意:在终止呼叫支路上对不支持SRTP / SDES的UE执行SRTP / SDES将导致连接建立失败,这可能是入站漫游的问题,其中运营商不能控制使用什么客户端,或者对于在相同网络中存在使用RTP的其他(非RCS)客户端的情况。
2.13.1.3.2 MSRP
MSRP is used in many RCS services which involve the exchange of images, files and instant messages (e.g. session based). Similar to RTP, MSRP is established through SDP exchanges in SIP signalling and it relies heavily on the security provided in signalling. The use of cryptographically strong random values appended to MSRP URIs exchanged within SDP provides binding between the SIP and MSRP sessions and any identities exchanged within SIP.
MSRP用于涉及图像,文件和即时消息(例如基于会话的)的交换的许多RCS服务中。 与RTP类似,MSRP通过SIP信令中的SDP交换建立,并且它大量依赖信令中提供的安全性。 附加到在SDP内交换的MSRP URI的加密强随机值的使用提供SIP和MSRP会话之间的绑定以及在SIP内交换的任何身份。
For RCS, the use of TLS mode as specified in [RFC4975] is recommended when MSRP is transported over an unsecure network (e.g. Wi-Fi). Consequently, a client configuration parameter to enable Message Session Relay Protocol over Transport Layer Security (MSRPoTLS) is specified in section A.2.10, and whether it is used or not can be configured differently for Wi-Fi access and cellular access.
对于RCS,当MSRP通过不安全的网络(例如Wi-Fi)传输时,建议使用[RFC4975]中指定的TLS模式。 因此,在A.2.10节中指定了用于启用消息会话中继协议通过传输层安全(MSRPoTLS)的客户端配置参数,并且是否使用它的配置参数可以针对Wi-Fi接入和蜂窝接入而不同地配置。
The RCS client shall use self-signed TLS certificates to produce fingerprints (e.g. secure hash) of the certificate which are exchanged during the SDP negotiation associated with the invitation and MSRP establishment procedure. The certificate fingerprint used for MSRP shall follow the same fingerprint mechanism specified in [RFC4572]. This binding of the certificate fingerprint to SIP signalling relies on the underlying security and trust provided by SIP signalling (e.g. IPsec, SIPoTLS (SIP over TLS), etc.). As a consequence, it is assumed that MSRPoTLS connections shall only happen when combined with the use of encrypted SIP signalling.
RCS客户端将使用自签名TLS证书来产生在与邀请和MSRP建立过程相关联的SDP协商期间交换的证书的指纹(例如安全散列)。 用于MSRP的证书指纹应遵循[RFC4572]中指定的相同的指纹机制。 证书指纹与SIP信令的这种绑定依赖于由SIP信令(例如IPsec,SIPoTLS(SIP over TLS)等)提供的基本安全性和信任。 因此,假设MSRPoTLS连接将仅在与使用加密的SIP信令相结合时发生。
When using MSRPoTLS, and with the following two objectives allow compliance with legal interception procedures, the TLS authentication shall be based on self-signed certificates and the MSRP encrypted connection shall be terminated in an element of the Service Provider network providing service to that UE. Mutual authentication shall be applied as defined in [RFC4572].
当使用MSRPoTLS并且具有以下两个目标允许遵守法律拦截过程时,TLS认证将基于自签名证书,并且MSRP加密连接将在向该UE提供服务的服务提供商网络的元件中终止。 应按照[RFC4572]中的定义应用相互认证。
Since the alternative connection model for MSRP shall be supported as specified in [RFC6135] (see section 2.8) the network will in some cases take the active role, and in some cases take the passive role, in the establishment of the TCP connection. Each peer (UE and network) shall take the same role (active or passive) in TLS as it took in TCP, so if the network has taken the passive role in TCP, it will also act as TLS server, as specified in [RFC6135]. When TLS is used, both endpoints shall exchange self-signed TLS certificates and fingerprints, as specified in [RFC4572].
由于MSRP的替代连接模型应当按照[RFC6135](见第2.8节)的规定支持,在某些情况下,网络将在建立TCP连接时发挥主动作用,并且在某些情况下采取被动作用。 每个对等体(UE和网络)在TLS中应该扮演与TCP中相同的角色(主动或被动),因此如果网络在TCP中具有被动角色,它也将作为TLS服务器,如[RFC6135 ]。 当使用TLS时,两个端点都应交换自签名TLS证书和指纹,如[RFC4572]中所述。
In RCS, and in accordance with [RFC4975], all UEs are mandated to support MSRPoTLS as defined in [3GPP TS 24.229-rel12] with certificate fingerprints as defined in [3GPP TS 33.328]. For terminating sessions, the P-CSCF (IMS ALG) decides based on local policy whether to apply MSRPoTLS towards the UE. A possible local policy is that the P-CSCF (IMS-ALG) invokes procedures related to MSRPoTLS for Wi-Fi access, but not for cellular access.
在RCS中,根据[RFC4975],所有UE被授权支持如[3GPP TS 24.229-rel12]中定义的具有如[3GPP TS 33.328]中定义的证书指纹的MSRPoTLS。 对于终止会话,P-CSCF(IMS ALG)基于本地策略来决定是否向UE应用MSRPoTLS。 可能的本地策略是P-CSCF(IMS-ALG)调用与用于Wi-Fi接入的MSRPoTLS有关但与蜂窝接入不相关的过程。
2.13.1.4 XCAP Authentication and Security / XCAP认证和安全
XML Configuration Access Protocol (XCAP) exchanges between the RCS client and the XDMS requires authentication and in most cases transport layer security.
RCS客户端和XDMS之间的XML配置访问协议(XCAP)交换需要认证,在大多数情况下需要传输层安全性。
The XCAP requests used in RCS shall use the OMA XDM architecture as defined in [XDM2.0_Core]. This means that all XCAP requests from RCS clients need to be authenticated via the Aggregation Proxy (AP) before being forwarded to an XDMS or to a Cross-Network Proxy. The XCAP authentication procedures between the RCS client and the Aggregation Proxy shall be handled as described in section 5.1 of [XDM2.2_Core], with the additional clarifications for RCS listed in this section.
在RCS中使用的XCAP请求应使用[XDM2.0_Core]中定义的OMA XDM架构。 这意味着来自RCS客户端的所有XCAP请求在转发到XDMS或跨网络代理之前需要通过聚合代理(AP)进行身份验证。 RCS客户端和聚合代理之间的XCAP身份验证过程应按照[XDM2.2_Core]的5.1节所述处理,本节中列出了RCS的其他说明。
For RCS clients enabled for VoLTE/VoWiFi (see section 2.9.1.1), the XCAP authentication shall be supported as follows:
对于启用VoLTE / VoWiFi的RCS客户端(见第2.9.1.1节),应支持XCAP认证,如下所示:
- When using single registration with VoLTE (i.e. using one single IMS registration for RCS and VoLTE), the same authentication specified for VoLTE use of XCAP, as defined in [PRD-NG.102] shall be supported.
当使用与VoLTE的单一注册(即,使用用于RCS和VoLTE的一个单一IMS注册)时,将支持如[PRD-NG.102]中所定义的针对XCAP的VoLTE使用指定的相同认证。 - When the RCS client uses a separate IMS registration from the VoLTE/VoWiFi client, then the XCAP authentication type used may be different than the VoLTE/VoWiFi client’s. If it is different, the XCAP authentication method used for RCS shall be HTTP digest based authentication as per section 5.1 of [XDM2.2_Core].
当RCS客户端使用来自VoLTE / VoWiFi客户端的单独的IMS注册时,则所使用的XCAP认证类型可以不同于VoLTE / VoWiFi客户端。 如果不同,用于RCS的XCAP认证方法将是基于HTTP摘要的认证根据[XDM2.2_Core]的第5.1节。 - For RCS clients (and IMS core) that support GAA, the RCS client shall use their AKA credential to fetch an HTTP digest credential using the 3GPP Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA). The RCS client authenticates to an Authentication Proxy (AP) over a TLS secured session using HTTP Digest as per section 5.1 of [XDM2.2_Core].
对于支持GAA的RCS客户端(和IMS核心),RCS客户端应使用其AKA凭证,使用3GPP通用引导架构(GBA)提取HTTP摘要证书。 RCS客户端使用HTTP Digest根据[XDM2.2_Core]的第5.1节通过TLS安全会话对身份验证代理(AP)进行身份验证。 - For RCS clients (and IMS core) that do not support GAA, the XCAP authentication type shall be HTTP digest. The RCS client shall use its pre-configured credential (e.g. username and password via the XDM configuration parameters in Annex A.1.3.1) to authenticate to the AP over a TLS secured session using HTTP Digest as per section 5.1 of [XDM2.2_Core].
对于不支持GAA的RCS客户端(和IMS核心),XCAP认证类型应为HTTP摘要。 RCS客户端应使用其预先配置的凭证(例如,通过附件A.1.3.1中的XDM配置参数的用户名和密码)通过使用HTTP Digest的TLS安全会话对AP进行认证,如[XDM2.2_Core ]。
For non-VoLTE/VoWiFi enabled RCS clients, the use of digest authentication over a TLS secured session shall be supported for XCAP authentication to the AP as per section 5.1 of [XDM2.2_Core].
对于非VoLTE / VoWiFi启用的RCS客户端,根据[XDM2.2 Core]的第5.1节,应支持通过TLS安全会话使用摘要认证,以用于向AP的XCAP认证。
When authentication type used for XCAP is HTTP Digest authentication:
当用于XCAP的认证类型是HTTP摘要认证时:
- RCS client may use the same credential (e.g. username and password) as SIP based Digest authentication when applicable.
RCS客户端可以在适用时使用与基于SIP的摘要认证相同的凭证(例如,用户名和密码)。NOTE: an RCS client may use different authentication types for SIP and XCAP.
注意:RCS客户端可能对SIP和XCAP使用不同的身份验证类型。 - The HTTP digest credentials (e.g. username and password) for XCAP specified in section A.1.3.1 shall be used.
应使用在A.1.3.1节中规定的XCAP的HTTP摘要凭证(例如用户名和密码)。
2.13.1.5 Common Message Store Authentication and Security / 公共消息存储认证和安全
The RCS client shall support the authentication and security mechanisms described in [RCS-CPM-MSGSTOR-ENDORS] for access to the Common Message Store using IMAP.
RCS客户端应支持[RCS-CPM-MSGSTORE-ENDORSE]中描述的认证和安全机制,以使用IMAP访问公共消息存储。
Authentication shall be based on username and password stored on the RCS client and the following Plaintext username and password sent using the LOGIN command as specified in [RFC3501].
认证应基于存储在RCS客户端上的用户名和密码,以及使用LOGIN命令发送的以下纯文本用户名和密码,如[RFC3501]中所述。
For SIM-based devices, the user name and password can either be configured through the MESSAGE STORE USER / PASSWORD configuration parameters defined in section A.1.4.3 or be derived through the Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) as described in section 4.1.4.1. For SIM-less devices, the credentials username and password shall always be provided as part of the configuration.
对于基于SIM的设备,用户名和密码可以通过A.1.4.3节中定义的MESSAGE STORE USER / PASSWORD配置参数进行配置,也可以通过通用引导架构(GBA)导出,如第4.1.4.1节所述 。 对于无SIM设备,凭证用户名和密码应始终作为配置的一部分提供。
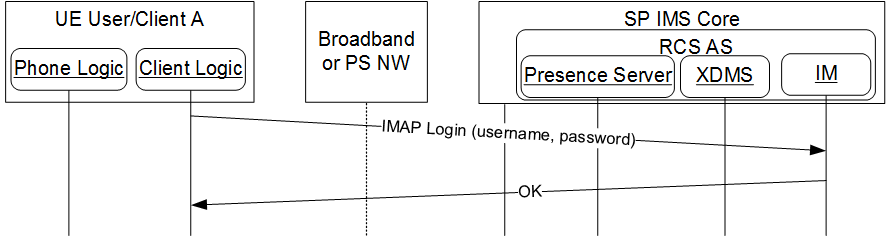
Figure 21: IMAP authentication with SASL or plain text login / 图21:使用SASL或纯文本登录的IMAP身份验证
TLS shall be used to provide message authentication, integrity protection and confidentiality for the IMAP protocol as specified in [RCS-CPM-MSGSTOR-ENDORS]. TLS must be established before any IMAP based authentication occurs using either the LOGIN or AUTHENTICATE command.
TLS应用于为[RCS-CPM-MSGSTOR-ENDORS]中规定的IMAP协议提供消息认证,完整性保护和机密性。 必须在使用LOGIN或AUTHENTICATE命令进行基于IMAP的身份验证之前建立TLS。
The Common Message Store server shall authenticate itself towards the RCS client using certificate based TLS authentication. The client shall support certificates based on a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for which the RCS client is pre-configured with a root or intermediate CA (which is recommended to be a public CA root authority) certificate in the signing chain of the certificate.
公共消息存储服务器将使用基于证书的TLS认证向RCS客户端认证自身。 客户端应支持基于公钥基础设施(PKI)的证书,对于该证书,RCS客户端在证书的签名链中预先配置有根或中间CA(其被推荐为公共CA根权限)证书。
2.13.2 Privacy / 隐私
2.13.2.1 Overview / 概述
A key element of promoting user adoption of RCS is gaining the user’s trust with regards to privacy. Service Providers need to provide security mechanisms to ensure unwanted parties cannot gain access to RCS user communications and provide adequate mechanisms to enable users to control the information they share. The key security measures to meet these requirements are outlined in section 2.13.1 and privacy controls are summarised in section 2.13.2.2.
促进用户采用RCS的关键因素是获得用户对隐私的信任。 服务提供商需要提供安全机制,以确保不必要的用户无法访问RCS用户通信,并提供足够的机制来使用户能够控制他们共享的信息。 满足这些要求的关键安全措施在2.13.1节中概述,隐私控制在第2.13.2.2节中概述。
2.13.2.2 Privacy controls / 隐私控制
Mechanisms provided in RCS to enable users to control their privacy are identified in this section.
在本节中标识了RCS中提供的用于使用户能够控制其隐私的机制。
2.13.2.2.1 Multidevice Privacy / 多设备隐私
Where an RCS user has RCS active across multiple devices this fact shall be obscured from other users.
当RCS用户在多个设备上具有RCS活动时,这个事实将被其他用户遮蔽。
NOTE: Where an RCS user has RCS active across multiple devices this fact cannot be obscured from devices of other users, since the GRUU and/or sip.instance feature tags shall automatically indicate this fact to these other devices.
注意:当RCS用户在多个设备上具有RCS活动时,这个事实不能被其他用户的设备遮挡,因为GRUU和/或sip.instance特征标签应自动向这些其他设备指示这一事实。
2.13.2.2.2 Presence information Privacy / 存在信息隐私
The RCS user shall have the option of controlling who they share their presence information with through a process of accepting, blocking or ignoring an invitation to establish a presence relationship (see section 3.7.4.5).
RCS用户可以通过接受,阻止或忽略建立存在关系的邀请来控制他们共享他们的存在信息的方式(见第3.7.4.5节)。
2.13.2.2.3 Video Privacy / 视频隐私
The RCS client shall provide the RCS user with control over when any camera on the device is active.
RCS客户端应向RCS用户提供对设备上的任何摄像机是否活动的控制。
2.13.2.2.4 Social Presence Information Privacy / 社交呈现信息隐私
The RCS user shall have the option to disable sharing of social presence information.
RCS用户可以选择禁用社交呈现信息的共享。
2.13.2.2.5 Network Address Book Privacy / 网络通讯簿隐私
The Service Provider shall ensure access control to the Network Address Book via a process of authentication.
服务提供商应通过认证过程确保对网络地址簿的访问控制。
2.13.2.2.6 Location Privacy / 位置隐私
The RCS user shall have the option to control sharing of location information (see section 3.10.1.2).
RCS用户应具有控制位置信息共享的选项(见第3.10.1.2节)。
2.13.2.2.7 Messaging and Chat / 消息和聊天
An RCS user shall have the option to control information communicated about their actions during messaging communications and chat sessions, including the suppression of “display” notifications and “IsComposing” notifications.
RCS用户可以选择在消息通信和聊天会话期间控制关于其操作的信息,包括抑制“display”通知和“IsComposing”通知。